December 2023
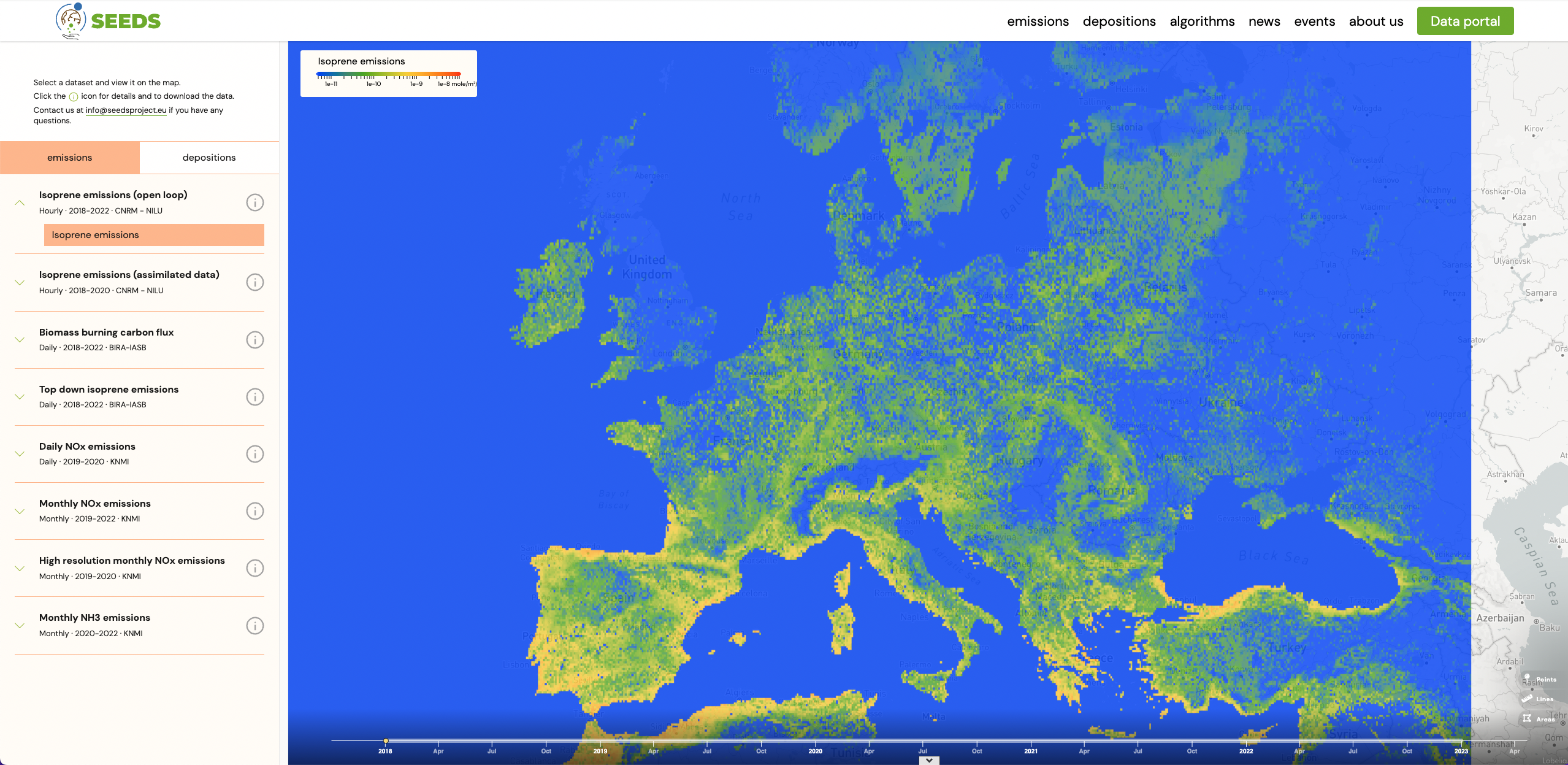
Developing the SEEDS data viewer, interview to Pau Moreno
Pau Moreno works as a software engineer at Lobelia, an SME based in Barcelona specialised in satellite technology, computational intelligence and data visualisation for climate action. His role in this project is to implement and deploy the SEEDS website, and to build a harmonised repository of all the datasets produced within the scope of this project.




